Welcome to Guangzhou Tongsen Electronic Technology Co., LTD. Website!
What is the SMT process?
These are the various steps in the SMT process. Each step in the SMT process is very important and determines the overall quality of the product. Considering this, electronics manufacturers are aware of and have implemented various optimizations, maintaining quality in each step of the SMT process.
What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT) process? In the electronics industry, SMT stands for Surface Mount Technology. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) process is a process of mounting electronic devices onto the surface of a printed circuit board. This process is very important in electronics manufacturing and is one of the techniques used by many electronics manufacturers. The SMT process is done by a surface mount technology component placement system (also known as pick and place machine).
This is done by placing surface mount devices (SMDs) onto a printed circuit board (PCB) with high precision and high speed. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry, enabling smaller, more efficient, and more cost-effective products. In the ever-evolving electronics industry, SMT, also known as surface mount technology, is very important and is widely adopted by many electronics manufacturers.
What steps are involved in surface mount assembly or SMT process?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a mainstay of modern electronics manufacturing. The main processes of SMT involve 5 major steps, including:
Stencil preparation;
Stencil printing;
Component placement;
Reflow soldering;
Cleaning and inspection;
These steps are usually followed by other processes such as SMT inspection and testing, cleaning, conformal coating, and final assembly, depending on the specific product requirements. Let's delve into each stage of the SMT process.
Stencil preparation:
What is a stencil in electronics? A stencil is a thin metal sheet with laser-cut holes that acts as a template for depositing solder paste onto the PCB. A well-prepared stencil is crucial for consistent solder paste deposition, ensuring good component placement and subsequent soldering.
First, a digital representation of the PCB's pad layout is made, and then a high-precision, programmed laser cutting machine is used to create the required apertures with exceptional accuracy.
The stencil is the mainstay that determines the overall quality and reliability of other subsequent steps in the SMT process.
Stencil printing or solder paste application:
Stencil printing is the initial step in the SMT process. The blueprint of the electronic circuit is shaped in this step. It involves depositing solder paste onto the printed circuit board (PCB) in preparation for component placement.
How is stencil printing done?
Stencil alignment:
The stencil, a thin metal sheet with laser-cut holes, is aligned with the PCB. The holes correspond to the pad locations on the PCB.
The stencil is firmly clamped onto the PCB.
Solder paste application:
Solder paste (a mixture of metal alloy powder and flux) is applied to the stencil.
A squeegee is moved across the stencil, forcing the solder paste through the apertures onto the pads of the PCB. The amount of solder paste deposited depends on factors such as stencil thickness, aperture size, and squeegee pressure.
Stencil removal:
Once the solder paste is deposited, the stencil is carefully removed from the PCB.
After stencil printing, the PCB is inspected to assess the printing quality.
Component placement:
It is simply the placement of electronic components onto the solder paste on the printed circuit board (PCB). This process is done with high precision and high speed. This method is usually done by an automated pick and place machine. Components are picked from feeders and accurately placed onto the designated pads, followed by a check for defects.
There are various types of component placement such as pick and place, chip shooters, and tape feeders. Component placement, precision, and speed affect the quality and efficiency of the final product.
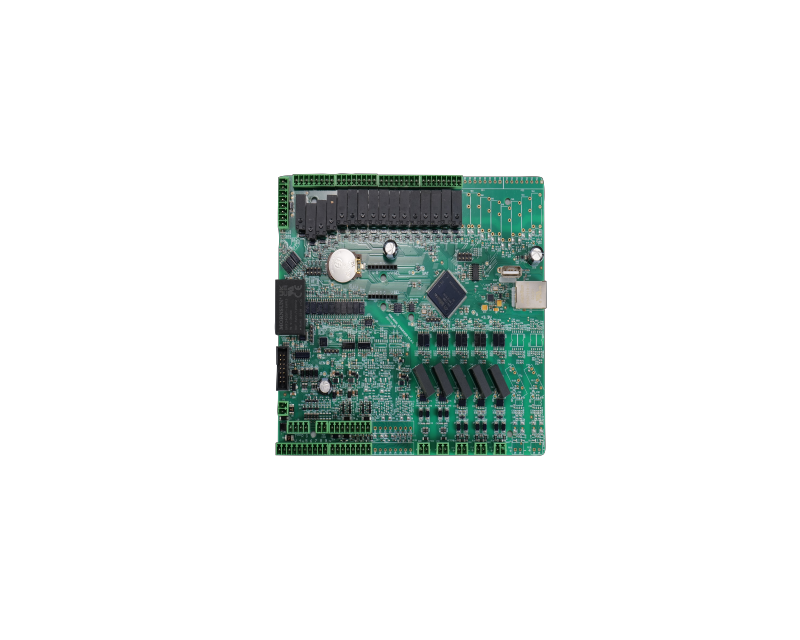

Reflow soldering:
This is the stage where the components are permanently bonded to the PCB. After all the above processes are completed, the PCB containing the solder paste, components, and other elements will be subjected to controlled heat. This controlled heat will help the solder paste melt and solidify, thus establishing an electrical connection between the components and the board. This is done under controlled heat because overheating may damage the electrical components.
Cleaning and inspection:
In this step, the reliability and longevity of the electronic product are ensured through cleaning and inspection in the SMT process.
The main purpose of cleaning is to remove flux residues, which are compounds left behind after the reflow soldering process. These residues can absorb moisture, leading to corrosion and electrical shorts.
PCB inspection is to ensure and guarantee the quality of the assembled PCB. It involves a series of checks to identify defects and ensure the overall quality of the assembled product.
Various methods employed by electronics manufacturing services include:
1) Visual inspection: A manual process where an operator checks the PCB for visible defects such as missing components, incorrect placement, solder bridges, or open circuits.
2) Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Uses cameras and image processing to detect defects such as missing components, incorrect component orientation, soldering defects, and component placement errors.
3) X-ray inspection (AXI): This non-destructive technique can identify hidden defects such as voids, solder bridges, and component cracks.
4) In-circuit testing (ICT): This method verifies the connectivity between components on the PCB.
These are the various steps in the SMT process. Each step in the SMT process is very important and determines the overall quality of the product. With this in mind, electronics manufacturers are aware and have various optimizations and maintain quality in each step of the SMT process.
RECOMMENDED NEWS
High-end Custom Services: SMT Chip Processing Meets Diverse Industry Needs





