Welcome to Guangzhou Tongsen Electronic Technology Co., LTD. Website!
Understanding basic circuit board components
Printed circuit boards are fundamental components of electronic devices. They provide the foundation for connecting and powering components, creating single, fully functional electronic circuits that power and control the device. Circuit boards come in single-sided and double-sided designs. The entire PCB is assembled by copper wires on the substrate. A printed circuit board without electronic components is considered a "bare board".
Printed Circuit Boards are fundamental components in electronic devices, forming the base for connecting and powering components to create a single, functional electronic circuit that powers and controls the device. Circuit boards come in single-sided and double-sided designs. The entire PCB is assembled by the copper traces on the substrate. A printed circuit, without the mounting of electronic components, is considered a "bare board."
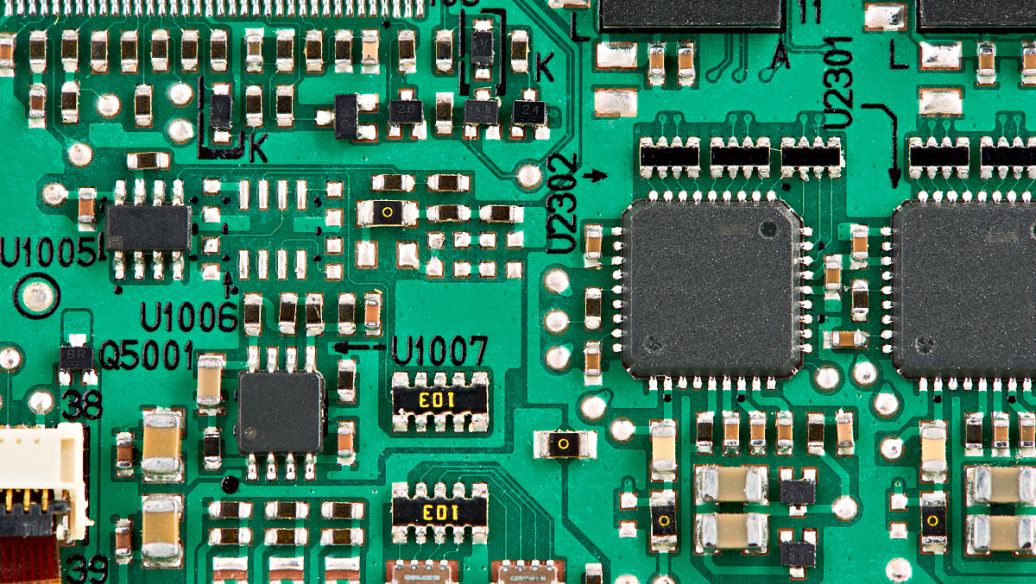
Bill of Materials for Circuit Boards
A. Mechanical Components
Depending on the type of metal chosen, mechanical circuit board components (including those made of aluminum, steel, copper, or bronze) are produced using a 'machining' method during manufacturing. These components differ from electrical components in that they provide additional support or auxiliary functions to the printed circuit board, rather than primarily serving to provide electrical functionality. Selecting and including appropriate mechanical components contributes to the overall mechanical integrity and stability of the printed circuit board.
B. Electrical Components
Electronic components play a supporting role, primarily making the soldering or wired electrical connections between components and the PCB easier. These components are crucial for providing electrical power within the electronic circuit. Furthermore, depending on how they emit electrical signals, they can be categorized as passive, active, or "other" PCB assembly components.
C. Passive Components
A large batch of components included in PCB components are passive components. Their main function is to react or save energy; they do not amplify or regulate electrical signals.
The list of passive electronic circuit board components is extensive; we will cover some of the important ones:
Capacitors
Capacitors are part of the components on a PCB, denoted by the letter "C" or the capacitance value (44mF). Their rated unit is Farads, commonly expressed in millifarads (mF) or microfarads (µF). They save energy in an electric field. Capacitors are essential components needed for temporarily storing electrical energy and releasing the stored energy. Capacitors retain charge by accumulating opposite charges on two conductive layers separated by an insulator. There are four main types of capacitors, namely ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, film capacitors, and paper capacitors. The type of capacitor used on a PCB depends on the conductor and dielectric material used. Ceramic capacitors are used at high density on PCBs, film capacitors are used to protect equipment from voltage surges, electrolytic capacitors are used when high capacitance is needed, and paper capacitors are used to block DC signals while allowing AC energy.
Fuses
Fuses are important components in PCB manufacturing and assembly. It is used to protect against current overload in the circuit. Fuses are denoted by the letter "F". You can easily identify a fuse because the fuse wire is visible within its glass casing, with metal caps at both ends. Keep in mind that if the fuse is a through-hole component, it may have the characteristics described above. However, when surface mount fuses are used, their characteristics usually involve an axial lead in a translucent tube directly above the fuse surface.
Resistors
Resistors are used to add resistance to a circuit board. Resistors have two passive terminals. The main function of a resistor is to impede the flow of current, rather than store energy. Additionally, resistors can also be used to restrict or block the flow of current into each linked component. Its rating is in Ohms and uses the resistance value. The ideal resistance value depends on the complexity of the PCB, the number of electronic components mounted on it, and the energy passing through it.
Previous
Previous :
RECOMMENDED NEWS
High-end Custom Services: SMT Chip Processing Meets Diverse Industry Needs






